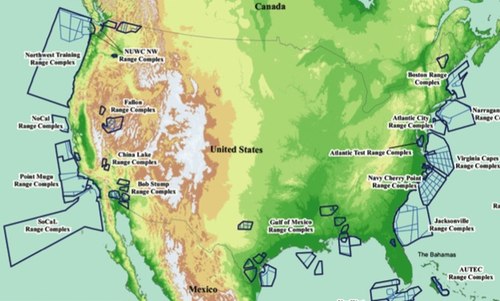
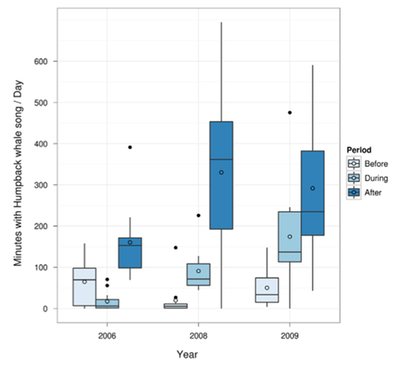
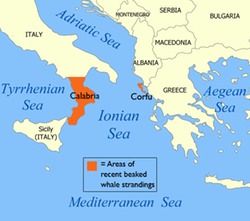
Whales can dampen hearing: implications for ocean noise concerns
Animal Communication, Bioacoustics, Effects of Noise on Wildlife, Ocean, Science Comments Off on Whales can dampen hearing: implications for ocean noise concernsYou may have noticed a recent flurry of press reports about research in Hawaii that begins to quantify a long-suspected quality of cetacean hearing: the ability to dampen hearing sensitivity so that loud sounds don’t cause damage. Given the extremely loud volume of many whale calls, which are meant to be heard tens or hundreds of miles away, researchers have long speculated that animals may have ways of protecting their ears from calls made by themselves or nearby whales, perhaps using a muscle response to reduce their hearing sensitivity (not unlike a similar muscular dampening mechanism in humans). Indeed, earlier studies by Paul Nachtigall’s team had found that some whales could do indeed reduce their auditory response to the sharp clicks they use for echolocation. In the new study, Nachtigall trained a captive false killer whale named Kina to reduce her hearing sensitivity by repeatedly playing a soft trigger sound followed by a loud sound. Eventually, she learned to prepare for the loud sound in advance by reducing her hearing sensitivity. “It’s equivalent to plugging your ears…it’s like a volume control,” according to Nachtigall.
Well, that sounds like a pretty useful trick, given all the concern about human sounds in the sea. And the media, led by the New York Times, jumped on board with headlines following on the Times‘ assertion that suggested whales already “are coping with humans’ din” using this method. (Among the exciting headline variations: Whales Can Ignore Human Noise, Whales Learning to Block Out Harmful Human Noise, and UH Scientists: Whales Can Shut Their Ears.)
Oops, they did it again! Grab some interesting new science and leap to apply a specific finding to a broad public policy question, often, as this time, giving us a false sense of security that the “experts” have solved the problem, so there’s no need to worry our little selves over it any more (as stressed in this NRDC commentary). To be fair, the Times piece included a few cautionary comments from both scientists and environmental groups, but the headline rippled across the web as the story was picked up by others.
Two key things to keep in mind: First, this whale was trained to implement her native ability, meant for use with her sounds or those of nearby compatriots, and to apply it to an outside sound made by humans. This doesn’t mean that untrained whales will do the same.
And second: If whales can dampen their hearing once a loud sound enters their soundscape, this could indeed help reduce the physiological impact of some loud human sounds, such as air guns or navy sonar. If indeed this ability translates to wild cetaceans, the best we could hope for is that it would minimize hearing damage caused by occasional and unexpected loud, close sounds that repeat. There would be no protection from the first blast or two, but perhaps some protection from succeeding ones; or, if the sound source was gradually approaching or “ramping up,” as often done with sonar and air guns, animals may be able to “plug their ears” before sounds reach damaging levels, if for some reason they can’t move away. Even then, the animals are very likely to experience rapidly elevated stress levels, as they would be less able to hear whatever fainter sounds they had been attending to before the intrusion. Yet research in the field suggests that most species of whales and dolphins prefer to keep some distance from such loud noise sources; this hearing-protection trick doesn’t seem to make them happy to hang around loud human sounds.
Most crucially, these occasional loud sounds are but a small proportion of the human noises whales are trying to cope with. Noise from shipping, oil and gas production activities, offshore construction, and more distant moderate sounds of air guns all fill the ocean with sound, reducing whales’ communication range and listening area, and likely increasing stress levels because of these reductions. This is the “din” of chronic moderate human noise in the sea, and Kina’s ability would not help her cope with any of it. We’re a long way from being able to rest easy about our sonic impacts in the oceans.
To end this rant with a bit of credit where due, here’s what may be the more important take-away from the Times article:
Peter Madsen, a professor of marine biology at Aarhus University in Denmark, said he applauded the Hawaiian team for its “elegant study” and the promise of innovative ways of “getting at some of the noise problems.” But he cautioned against letting the discovery slow global efforts to reduce the oceanic roar, which would aid the beleaguered sea mammals more directly.

 In addition to three environmental organizations, the Native Village of Chickaloon is party to the lawsuit, saying that NMFS did not fulfill necessary consultation with the tribe, and noting that while the tribe is barred from its traditional hunts due to declining beluga numbers, the permits allow oil and gas development to put whales at risk.
In addition to three environmental organizations, the Native Village of Chickaloon is party to the lawsuit, saying that NMFS did not fulfill necessary consultation with the tribe, and noting that while the tribe is barred from its traditional hunts due to declining beluga numbers, the permits allow oil and gas development to put whales at risk. Bernie Krause’s new book,
Bernie Krause’s new book, 
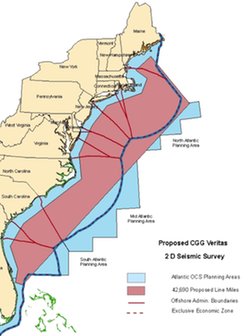 I’ve yet to dig into the PEIS to examine its alternatives or proposed mitigation measures, but a quick look at maps illustrating applications already received from oil and gas exploration companies affirms that the entire east coast could become an active seismic survey zone (the map at left is one of nine applications; there is much overlap among them).
I’ve yet to dig into the PEIS to examine its alternatives or proposed mitigation measures, but a quick look at maps illustrating applications already received from oil and gas exploration companies affirms that the entire east coast could become an active seismic survey zone (the map at left is one of nine applications; there is much overlap among them). A Canadian frigate used its mid-frequency active sonar this week during a training exercise in Haro Strait, north of San Juan Island and south of Vancouver Island. The sonar emissions from the HMCS Ottowa (right) were picked up by whale researchers at Beam Institute, who raised concerns about sonar use in an area designated by the US as critical habitat for orcas. You can read a detailed report from Beam, including sonograms and MP3 files of the sounds heard,
A Canadian frigate used its mid-frequency active sonar this week during a training exercise in Haro Strait, north of San Juan Island and south of Vancouver Island. The sonar emissions from the HMCS Ottowa (right) were picked up by whale researchers at Beam Institute, who raised concerns about sonar use in an area designated by the US as critical habitat for orcas. You can read a detailed report from Beam, including sonograms and MP3 files of the sounds heard,  A fascinating new study provides the first direct evidence that shipping noise may increase stress levels in whales. During the days after the World Trade Center attacks, global shipping was halted; a team of researchers studying right whales in the Bay of Fundy decided to go ahead and continue collecting fecal samples, and were struck by how peaceful it was: Rosalind Rolland
A fascinating new study provides the first direct evidence that shipping noise may increase stress levels in whales. During the days after the World Trade Center attacks, global shipping was halted; a team of researchers studying right whales in the Bay of Fundy decided to go ahead and continue collecting fecal samples, and were struck by how peaceful it was: Rosalind Rolland