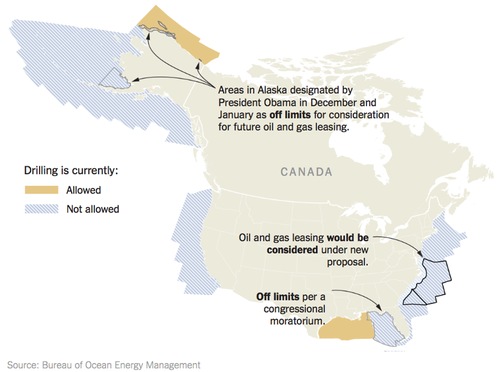
Scientists object to new Atlantic oil/gas exploration plans
Bioacoustics, Ocean energy, Seismic Surveys Add commentsA letter from 75 leading bio-acoustics researchers urges President Obama to derail current plans to open much of the US eastern seaboard to oil and gas exploration and development. Last year, the Department of Interior opened the door to new seismic surveys from Delaware to Georgia, which will clarify which areas of the continental shelf are most promising as drilling sites; these could begin as soon as this year or next. So far, nine applications have been filed for surveys, all 50 miles or more offshore. In January of this year, Interior announced plans to issue drilling leases beginning in 2017, with the initial five-year leasing period targeting roughly the same region (UPDATE, 3/15/16: Interior cancels lease planning); in conjunction with opening this area, development was banned in some Alaskan waters (small areas off the north slope and a larger area in SW Alaska).
 All this has spurred much public outcry, and in March an impressive array of ocean scientists from dozens of universities and research organizations around the world took the unprecedented step of sending a letter to President Obama expressing deep concern about the acoustic impacts of these plans. “The magnitude of the proposed seismic activity is likely to have significant, long-lasting and widespread impacts on the reproduction and survival of fish and marine mammal populations in the region, including the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale, of which only 500 remain,” say these researchers (see the full letter).
All this has spurred much public outcry, and in March an impressive array of ocean scientists from dozens of universities and research organizations around the world took the unprecedented step of sending a letter to President Obama expressing deep concern about the acoustic impacts of these plans. “The magnitude of the proposed seismic activity is likely to have significant, long-lasting and widespread impacts on the reproduction and survival of fish and marine mammal populations in the region, including the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale, of which only 500 remain,” say these researchers (see the full letter).
New dynamic maps from NOAA’s new Cetacean & Sound Mapping project indicate that these right whales use the southeast coast intensively in January and February, and are present along much of the coast in March and April moving north, and November and December heading south. Only during the months of June-October are these whales mostly in northern waters away from the region currently being targeted. Of course, other marine species are present year-round.
The Department of Interior suggests that since all activity will be more than 50 miles offshore, it should not interfere with commercial or recreational fishing, or near-shore areas of critical habitat; however, airgun sounds are often audible at much greater distances than that. Energy companies also stress that heavy seismic survey activity in the Gulf of Mexico has co-existed for decades with both commercial and recreational fishing activity.
While initial push-back has largely been focused on the seismic surveys, which use pulses of loud sound to image deep below the seafloor (here’s a good explainer), the longer-term acoustic footprint of oil development is likely to also be significant. Ocean Conservation Research has been focusing on this for several years, tracking the new generation of seafloor processing facilities that are making deep-water development possible:
Much of the technology that makes deepwater drilling possible hinges on creating pre-refineries on the sea floor. These include seafloor separators, reinjection pumps, multi-phase pumps and other equipment all operating under extreme pressures and often very high (and noisy) differential pressures. Additionally these deepwater operations are typically performed from dynamically stabilized drill ships and “semi-submersible” platforms that are always churning away.
